Qual é a diferença entre servo-embreagem e servo-freio?
Jul 17, 2025
Qual é a diferença entre servo-embreagem e servo-freio?
1. Diferença de posicionamento de função
O servo-embreador é projetado para transmissão manual. Suas principais funções são:
Aumente a força do pedal de 5 a 8 vezes (a relação de reforço dos carros comuns é de cerca de 1:6,5)
Ajuda a separar completamente a placa de fricção (precisão do controle do curso ± 0,5 mm)
Obtenha retorno rápido (tempo de reinicialização ≤0,3 segundos)
Por exemplo, o
servo-embreagem Isuzu
Os sistemas são projetados especificamente para atender às demandas operacionais de veículos pesados, oferecendo desempenho consistente em ambientes de alta carga.
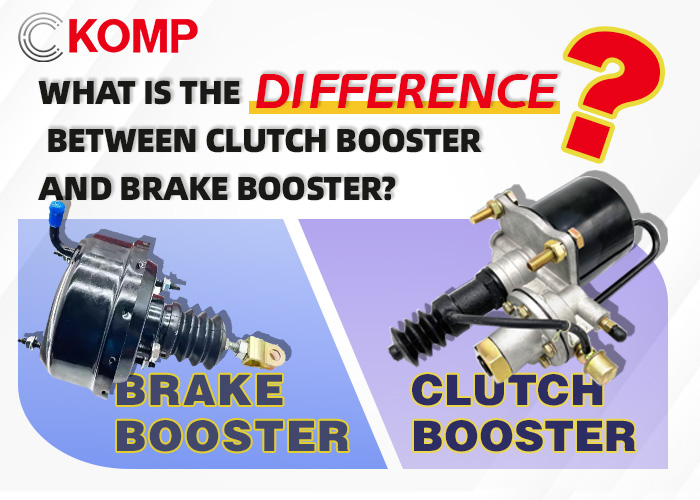 O servo-freio serve ao sistema de frenagem:
A taxa de reforço típica é superior a 1:10 (os modelos SUV podem chegar a 1:12)
É necessário estabelecer uma pressão hidráulica contínua (a pressão de trabalho é geralmente de 2 a 4 MPa)
Equipado com função de assistência de frenagem de emergência (a pressão aumenta repentinamente quando o sistema EBA intervém)
2. Comparação de princípios estruturais
Características estruturais do servo-embreagem:
Usando câmara de ar de diafragma (diâmetro 80–120 mm)
O diâmetro do pistão hidráulico é geralmente de 18 a 25 mm
Acumulador integrado (pressão pré-armazenada 0,4–0,6 MPa)
A estrutura típica inclui:
Corpo da válvula de controle
Cilindro hidráulico
Câmara de pressão de ar
Mecanismo de haste de pressão
A China tornou-se uma importante fonte destes produtos. Uma
fábrica de servo-embreagem na China
normalmente se especializa em produção em larga escala com rigoroso controle de qualidade, o que a torna uma fornecedora competitiva no mercado global de reposição.
Componentes principais do servofreio:
Câmara de vácuo (diâmetro 200–300 mm)
Design de diafragma duplo (padrão para modelos modernos)
Bomba de vácuo eletrônica (essencial para veículos de nova energia)
Subsistemas principais:
Válvula de retenção de vácuo
Grupo de haste de pressão de entrada
Mecanismo de placa de reação
Interface do cilindro mestre hidráulico
Principal
fabricantes de servo-freios
foco em desempenho, certificação de segurança e integração eletrônica para atender à crescente demanda em plataformas tradicionais e de veículos elétricos.
O servo-freio serve ao sistema de frenagem:
A taxa de reforço típica é superior a 1:10 (os modelos SUV podem chegar a 1:12)
É necessário estabelecer uma pressão hidráulica contínua (a pressão de trabalho é geralmente de 2 a 4 MPa)
Equipado com função de assistência de frenagem de emergência (a pressão aumenta repentinamente quando o sistema EBA intervém)
2. Comparação de princípios estruturais
Características estruturais do servo-embreagem:
Usando câmara de ar de diafragma (diâmetro 80–120 mm)
O diâmetro do pistão hidráulico é geralmente de 18 a 25 mm
Acumulador integrado (pressão pré-armazenada 0,4–0,6 MPa)
A estrutura típica inclui:
Corpo da válvula de controle
Cilindro hidráulico
Câmara de pressão de ar
Mecanismo de haste de pressão
A China tornou-se uma importante fonte destes produtos. Uma
fábrica de servo-embreagem na China
normalmente se especializa em produção em larga escala com rigoroso controle de qualidade, o que a torna uma fornecedora competitiva no mercado global de reposição.
Componentes principais do servofreio:
Câmara de vácuo (diâmetro 200–300 mm)
Design de diafragma duplo (padrão para modelos modernos)
Bomba de vácuo eletrônica (essencial para veículos de nova energia)
Subsistemas principais:
Válvula de retenção de vácuo
Grupo de haste de pressão de entrada
Mecanismo de placa de reação
Interface do cilindro mestre hidráulico
Principal
fabricantes de servo-freios
foco em desempenho, certificação de segurança e integração eletrônica para atender à crescente demanda em plataformas tradicionais e de veículos elétricos.
3. Diferenças nas características de trabalho
Parâmetros
|
Reforço de embreagem
|
Servo-freio
|
Pressão de trabalho
|
0,8–1,2 MPa
|
2–4 MPa
|
Tempo de resposta
|
50–80 ms
|
30–50 ms
|
AVC
|
120–150 mm
|
40–60 mm
|
Faixa de temperatura
|
-30℃~120℃
|
-40℃~150℃
|
4. Comparação de modos de falha
Falhas comuns do servo-embreagem:
Vazamento de pressão do óleo hidráulico (envelhecimento do anel de vedação)
Falha de assistência (pressão insuficiente do acumulador)
Retorno lento do pedal (fadiga da mola de retorno)
Falhas típicas do servo-freio:
Vazamento de vácuo (diafragma danificado)
Assistência irregular (placa de reação desgastada)
Pedal duro (válvula de retenção bloqueada)
5. Pontos de manutenção
Manutenção do servo-embreagem:
Verifique o óleo hidráulico a cada 30.000 quilômetros
Exaustão de ar regularmente (recomendado a cada 2 anos)
Preste atenção ao curso livre do pedal (padrão 10–15 mm)
Manutenção do servo-freio:
Inspeção anual da linha de vácuo
Mantenha o compartimento do motor limpo
Preste atenção ao ciclo de troca do fluido de freio (2 anos/40.000 quilômetros)
Wuhu Compass Autoparts Technology Co., Ltd é um fabricante de servo-freios e servo-embreagens na China. KOMP é sua marca. A KOMP pode fornecer servo-embreagens e servo-freios com preço de fábrica e fornecer garantia de um ano ou 30.000 km. Se você quiser comprar produtos de boa qualidade e acessíveis, a KOMP é sua boa escolha!
